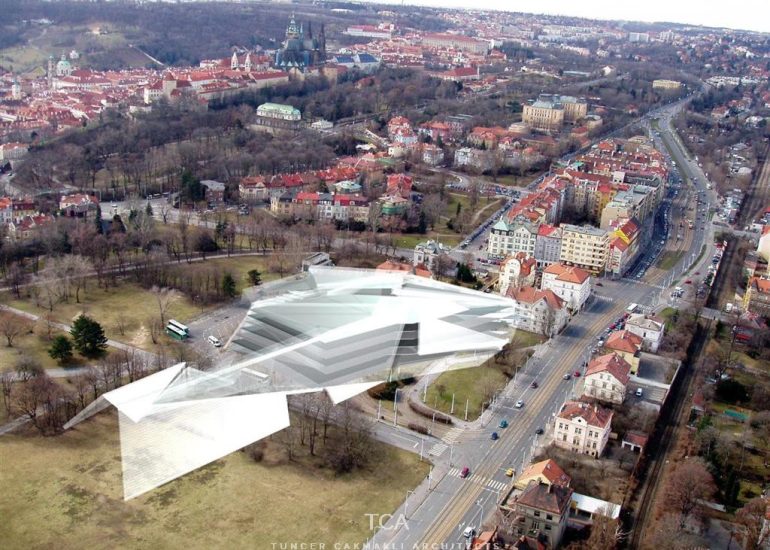
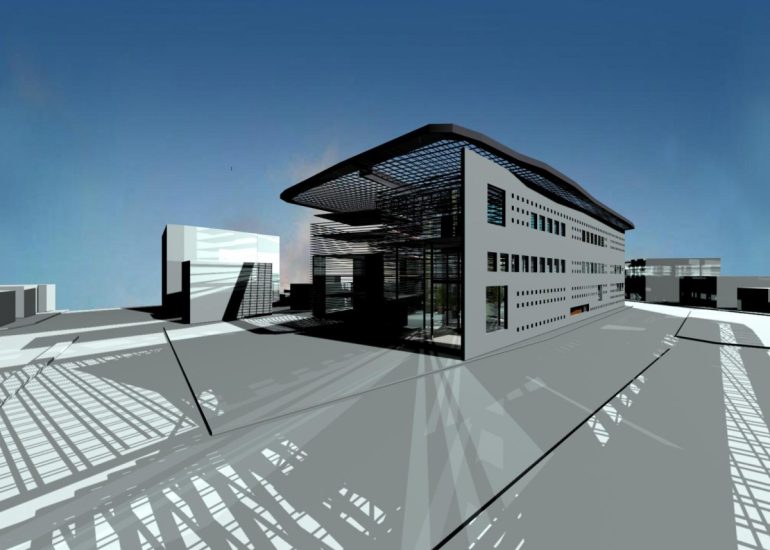
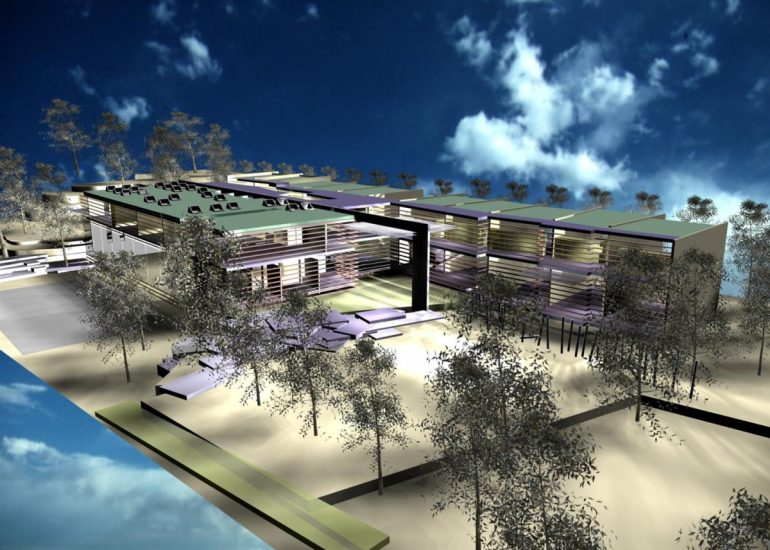
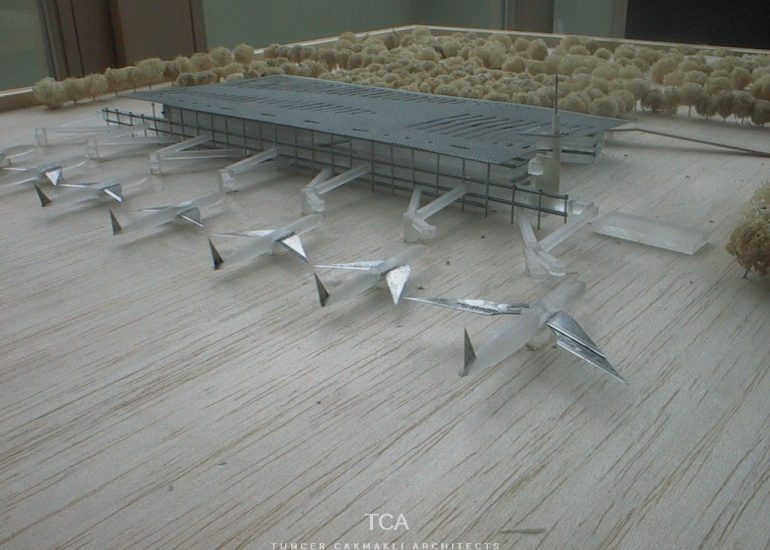
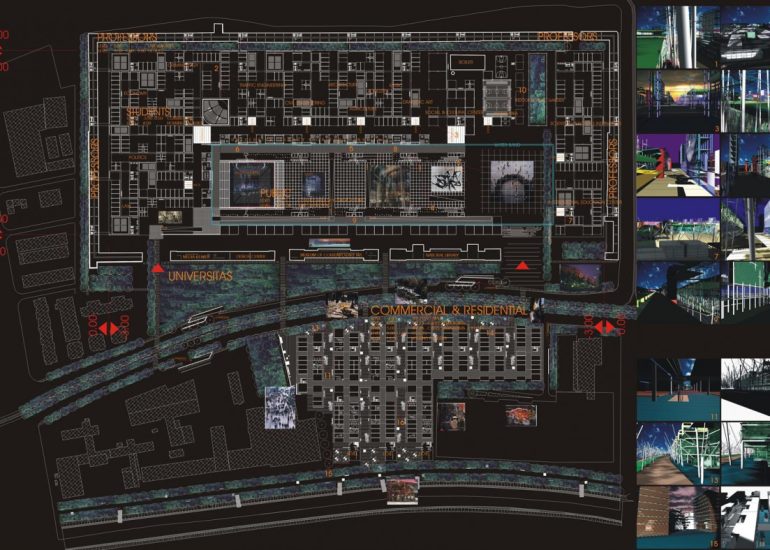
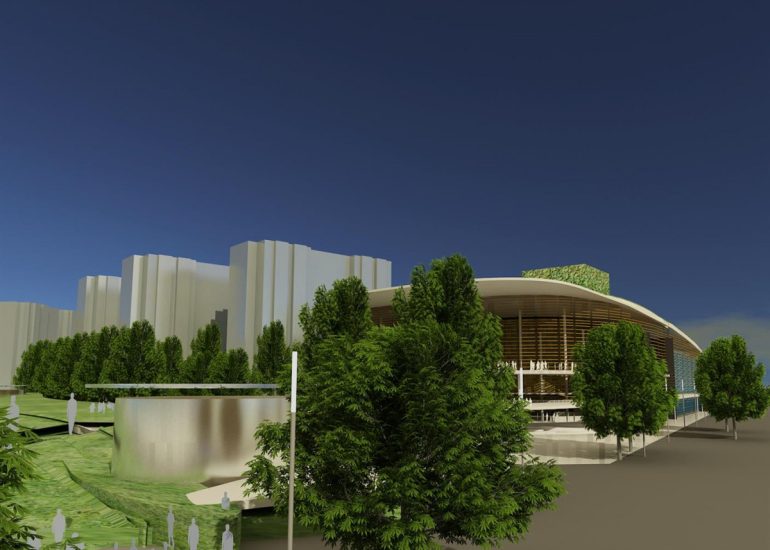
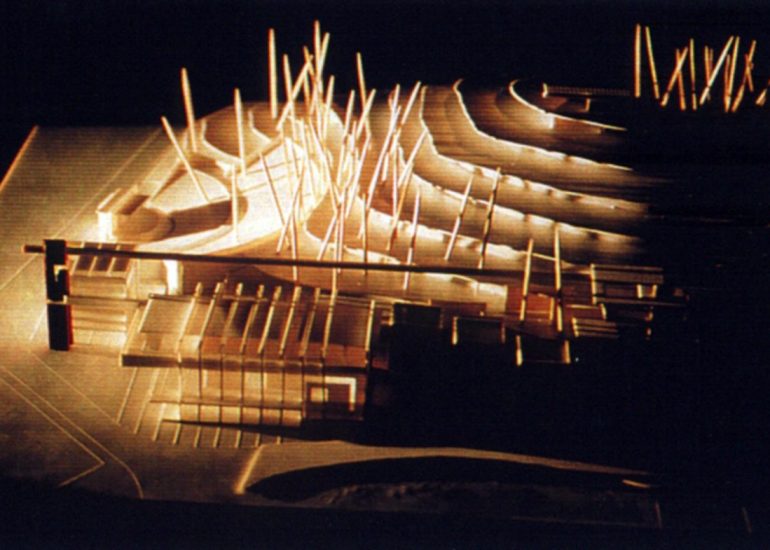
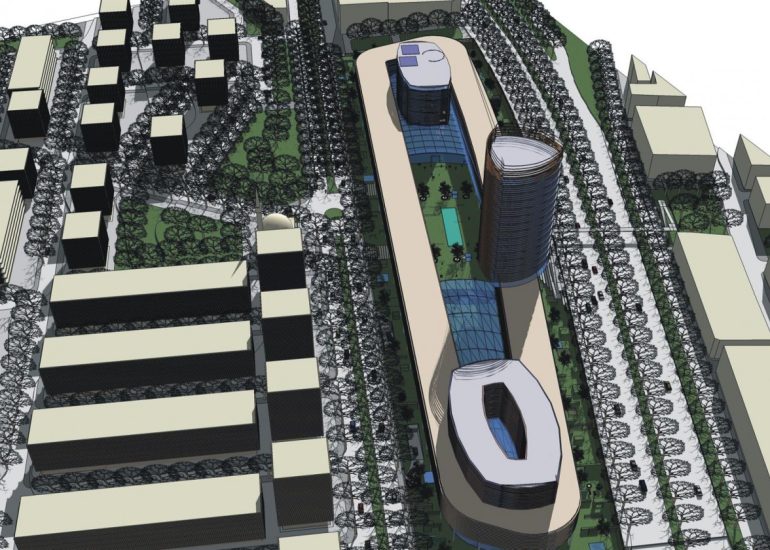
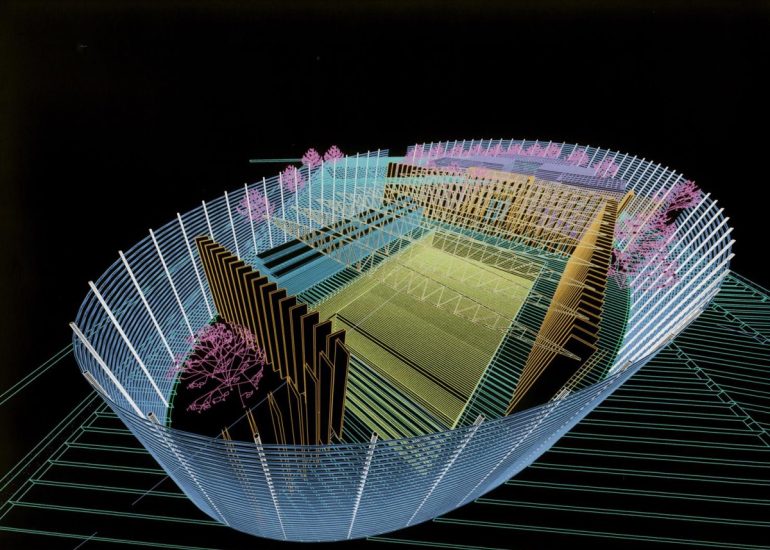
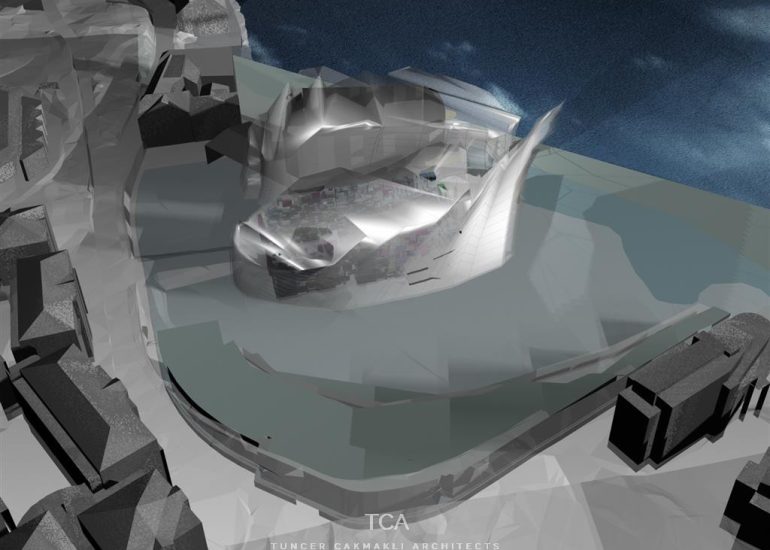
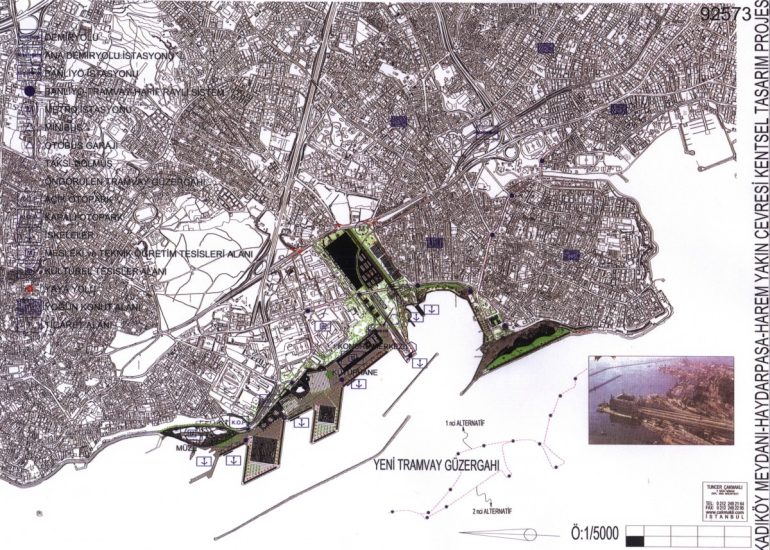
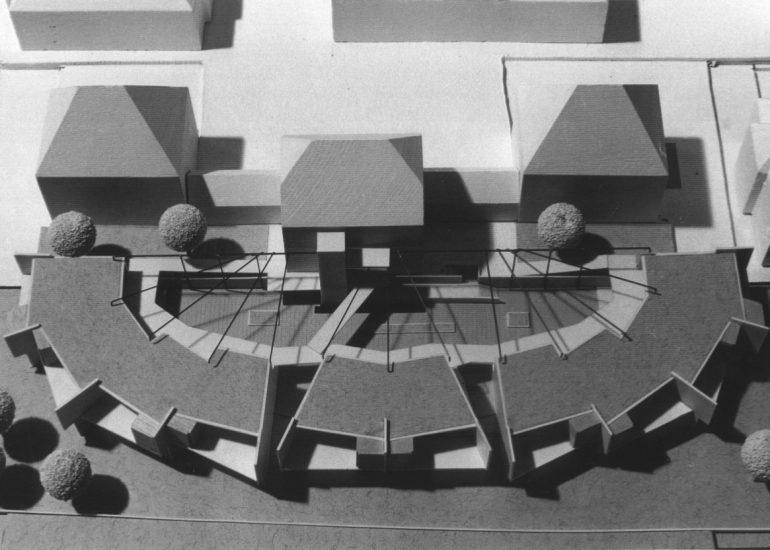
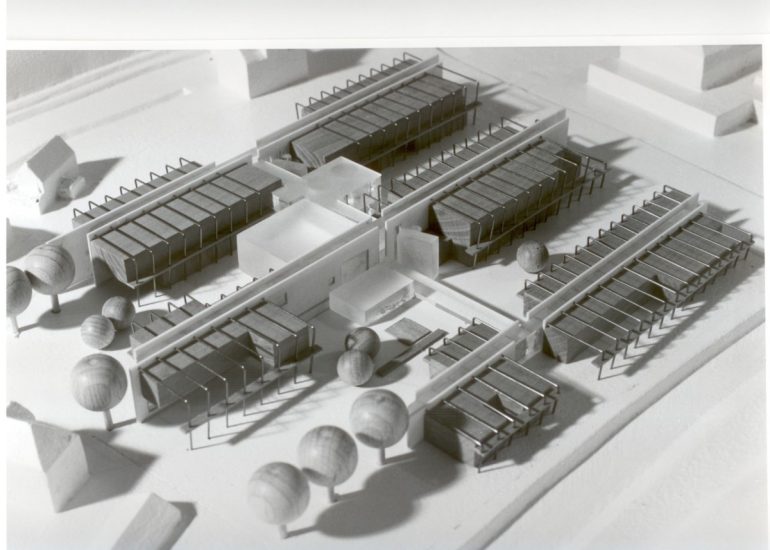
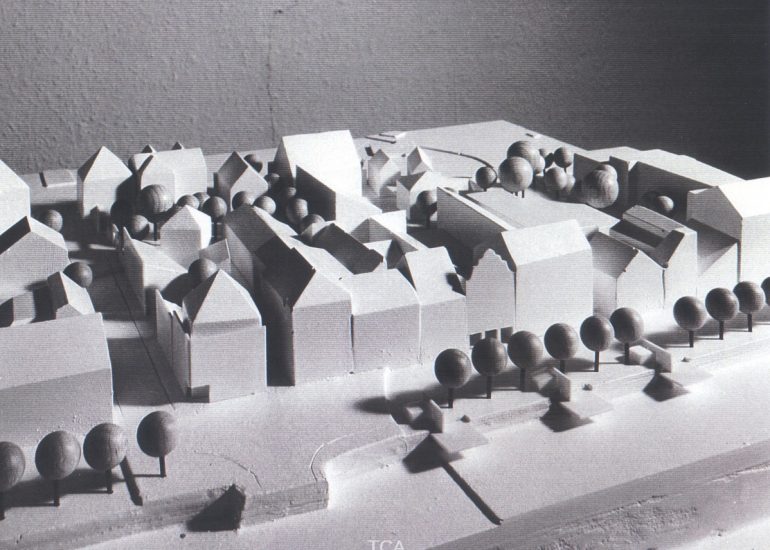
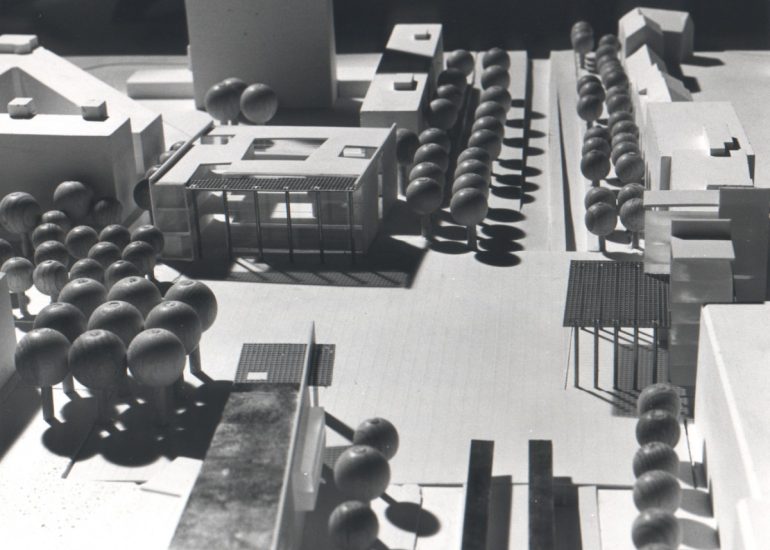
TCA - DESIGN PROCESS MODELS
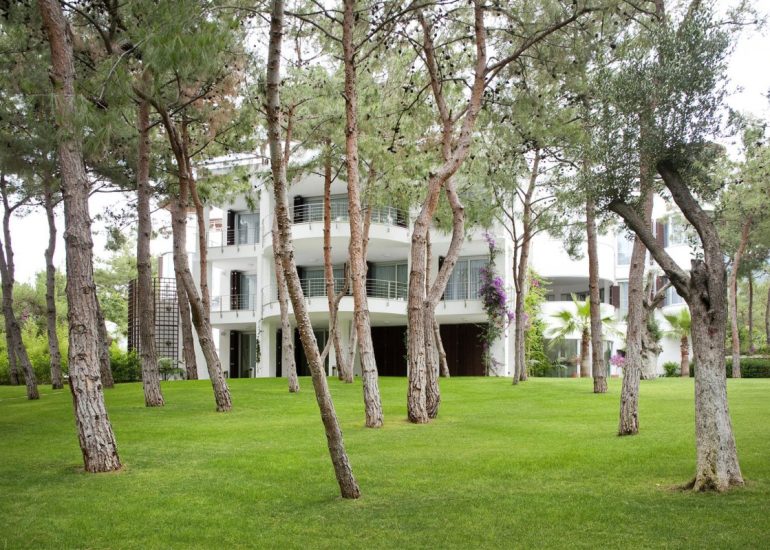
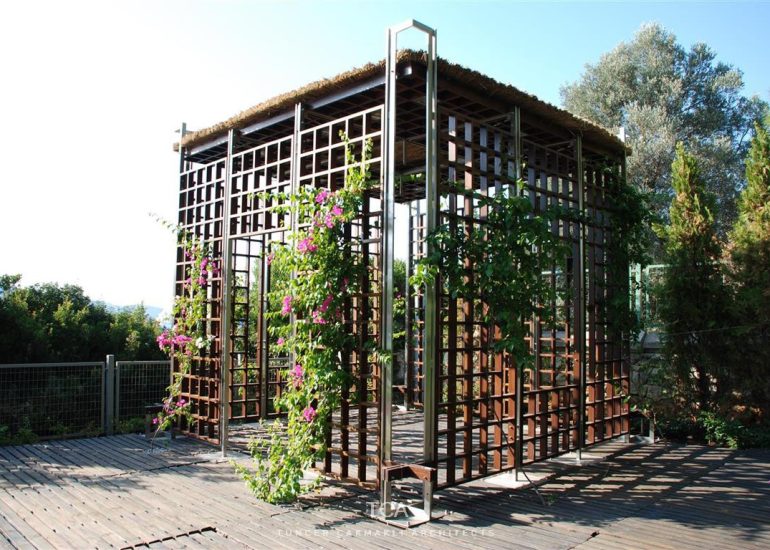
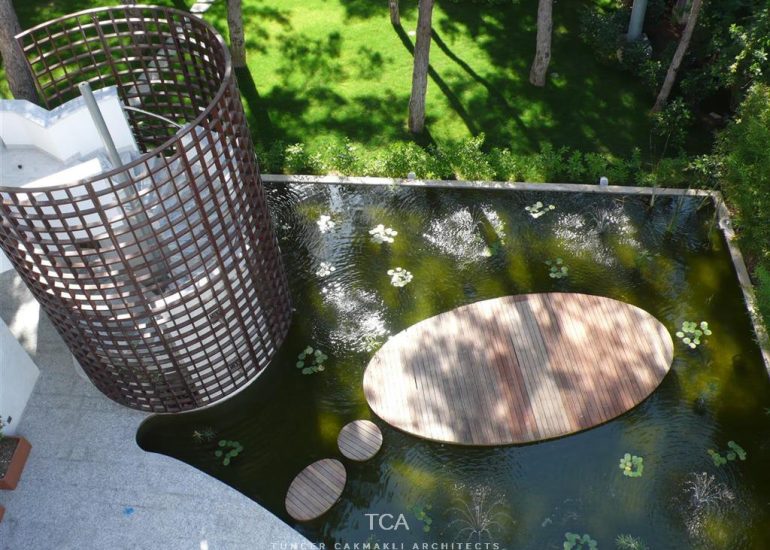
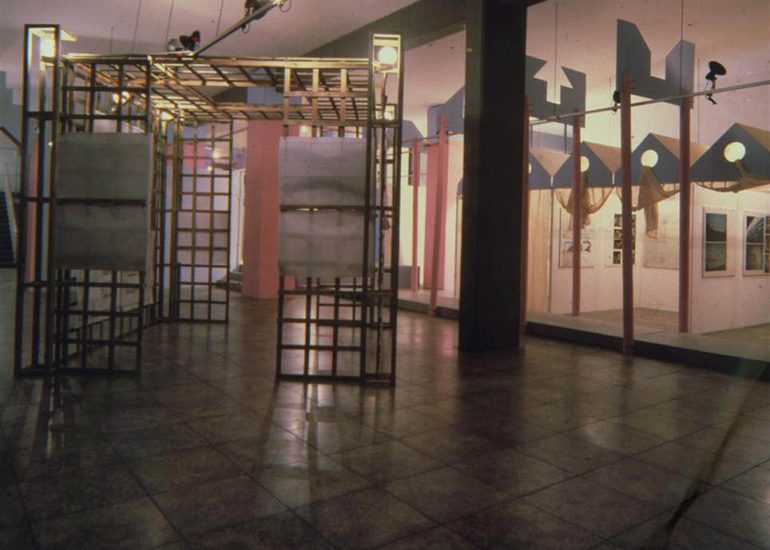
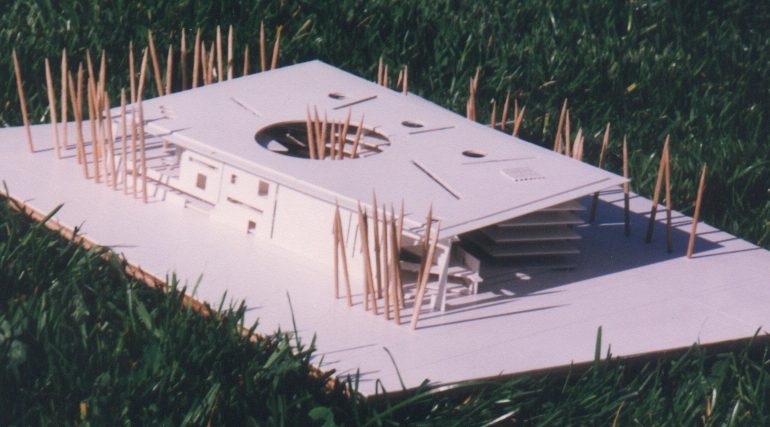
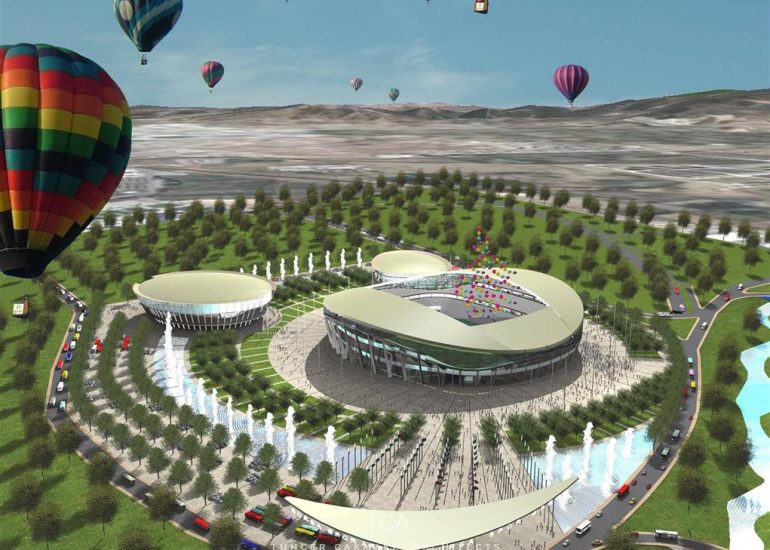
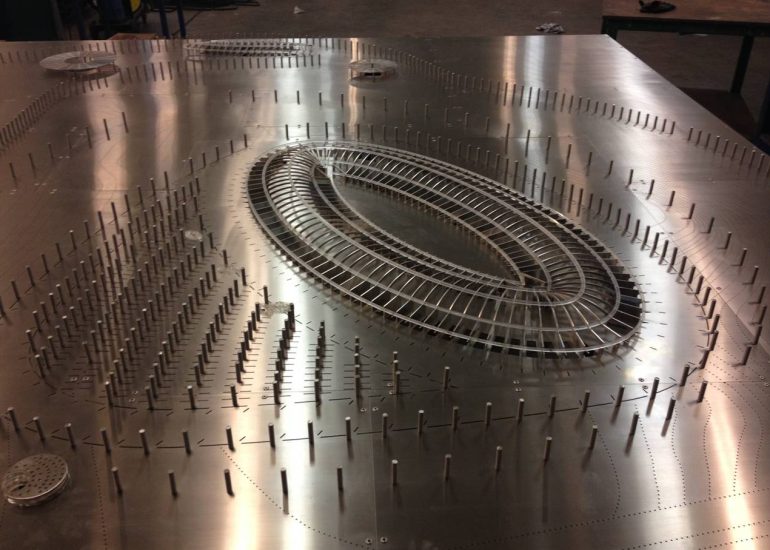
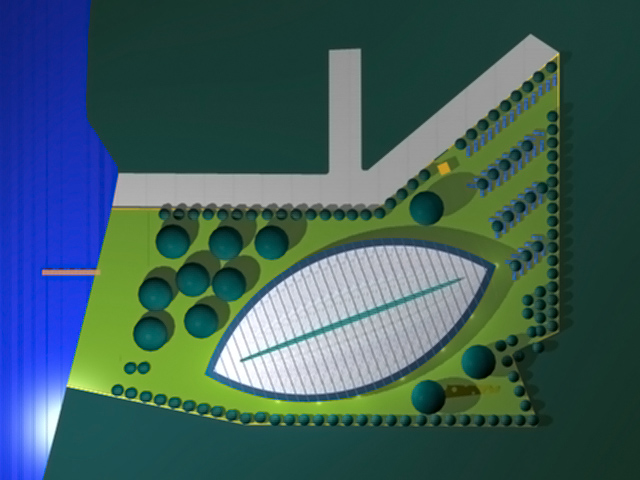
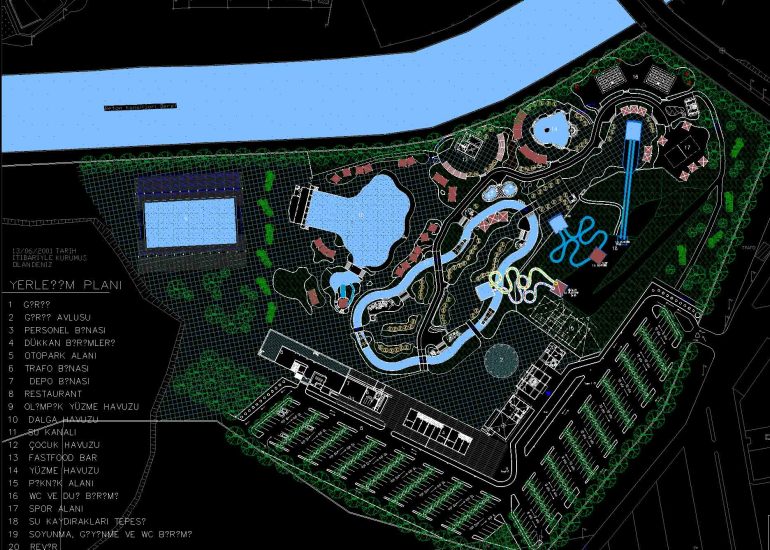
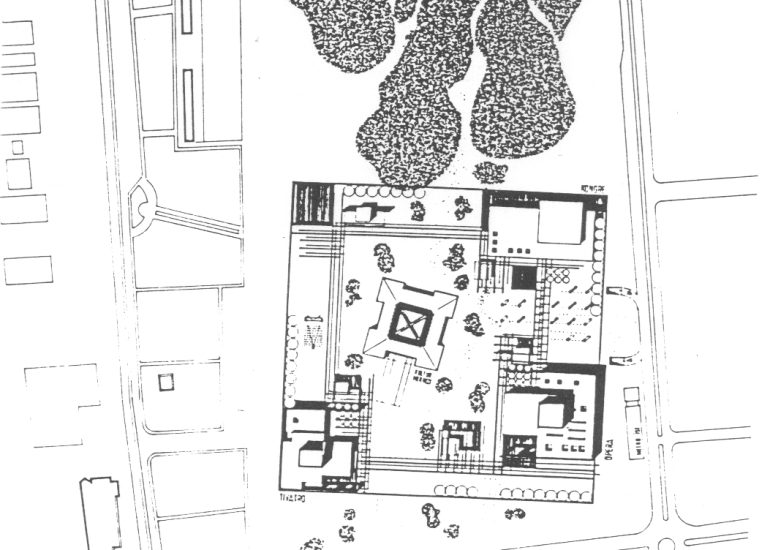
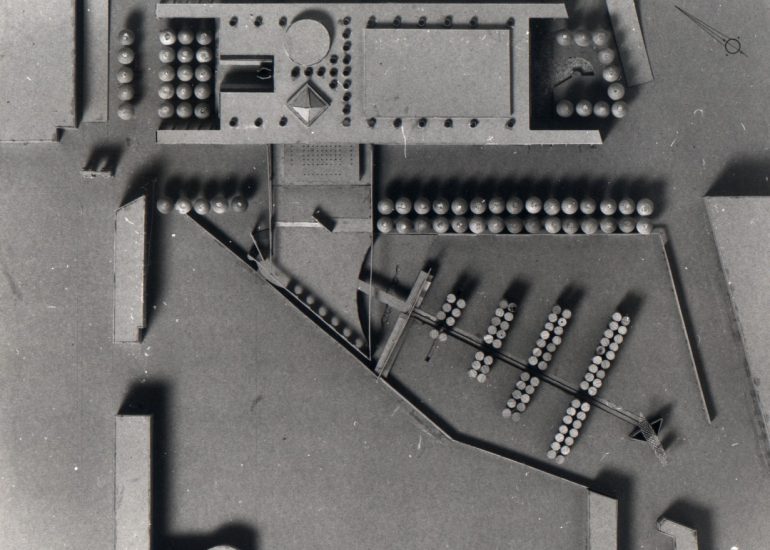
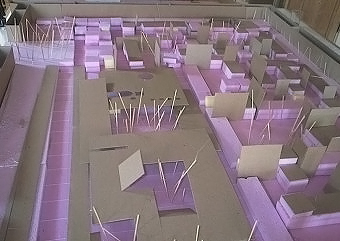
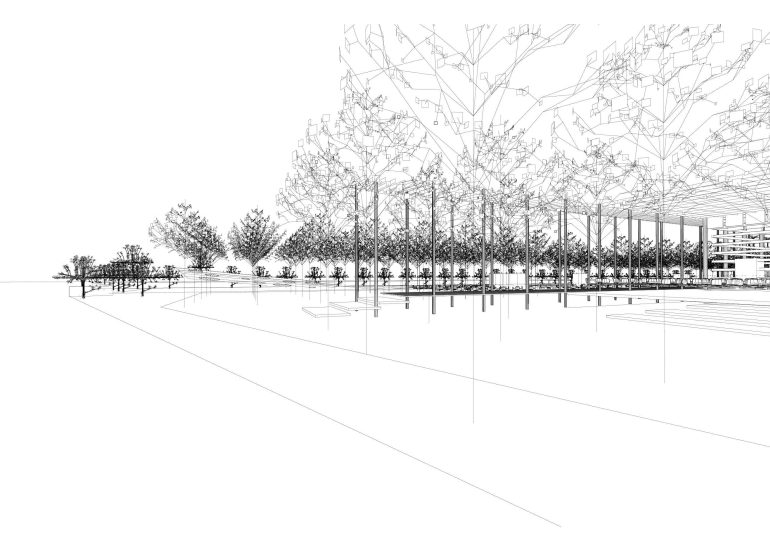
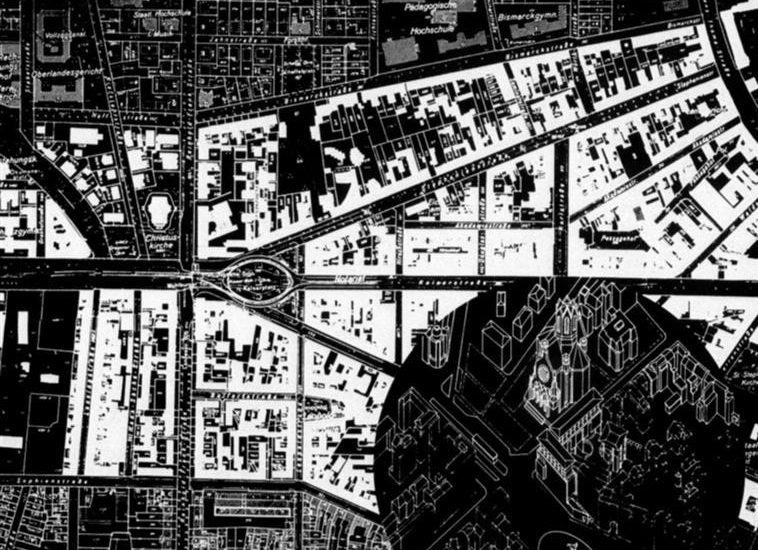
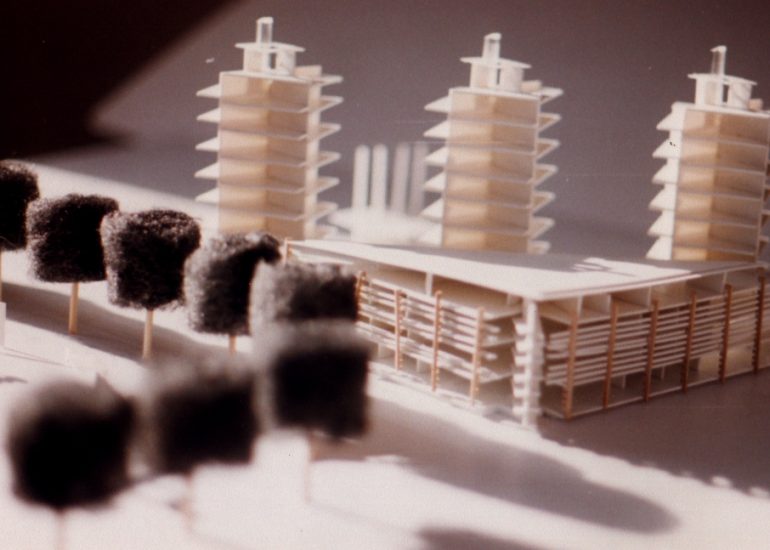
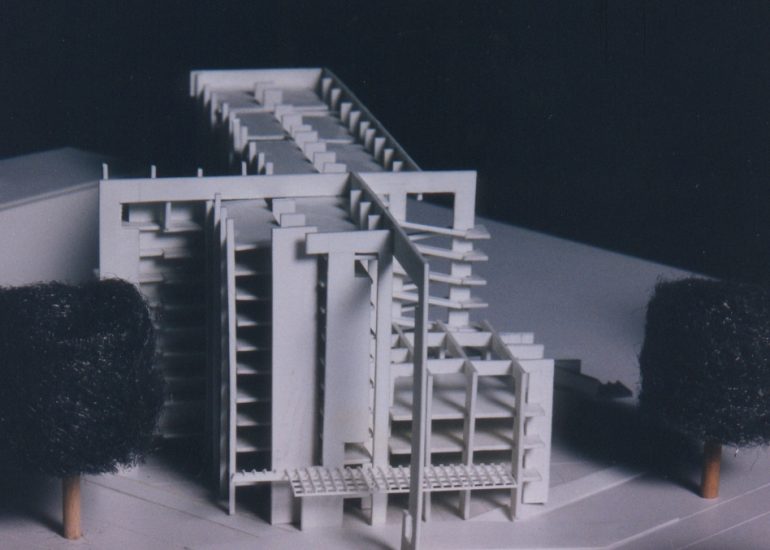
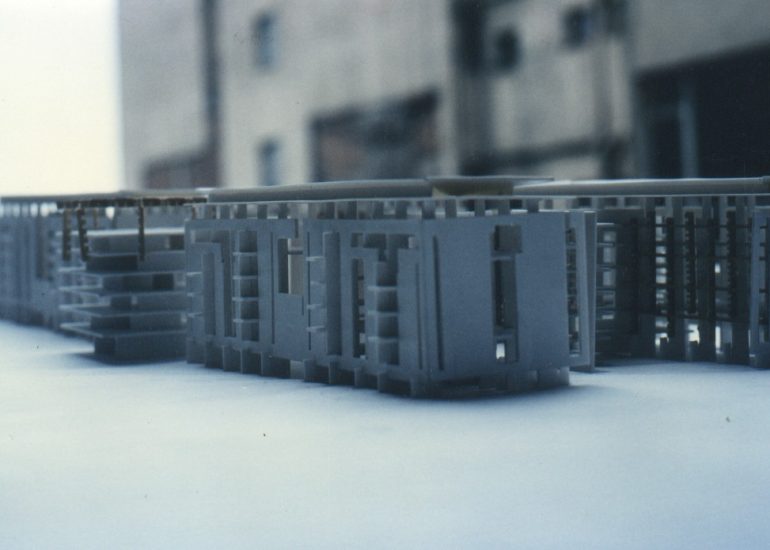
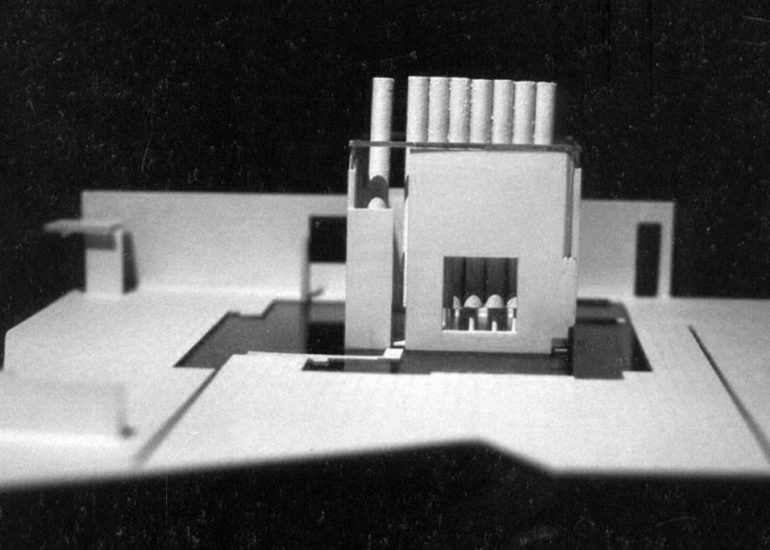
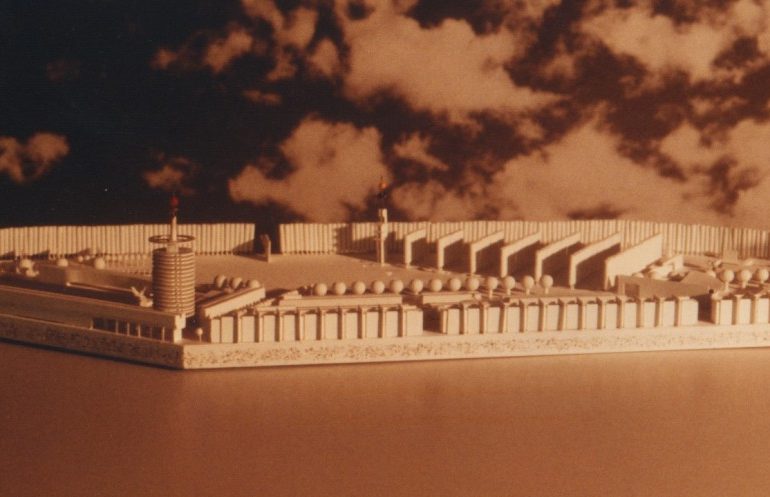
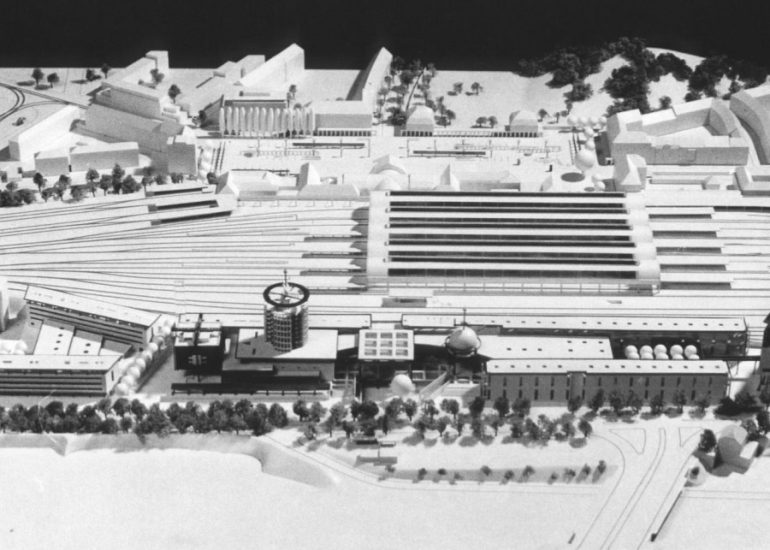
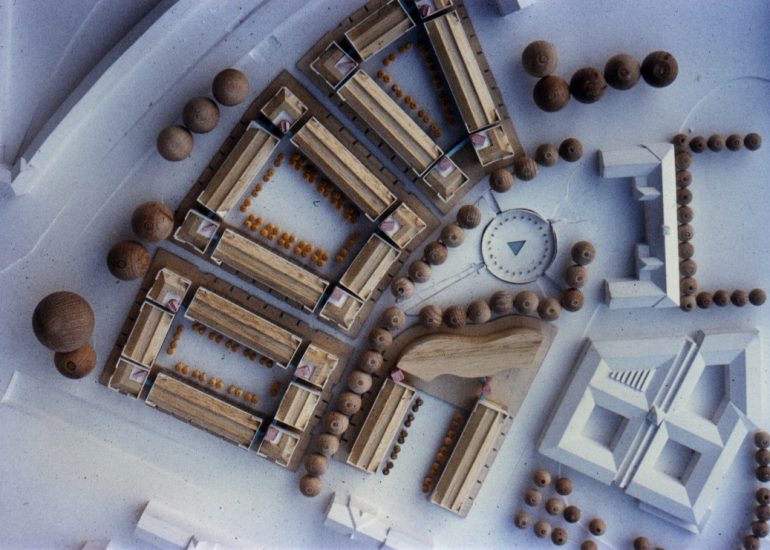
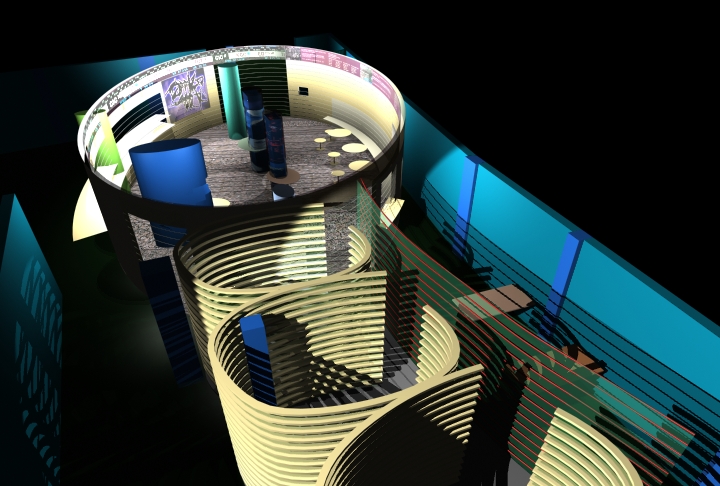
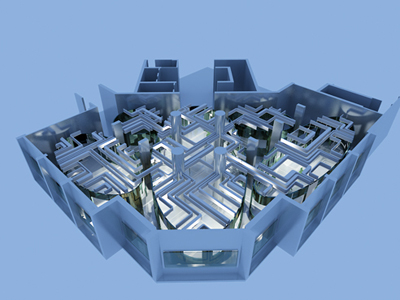
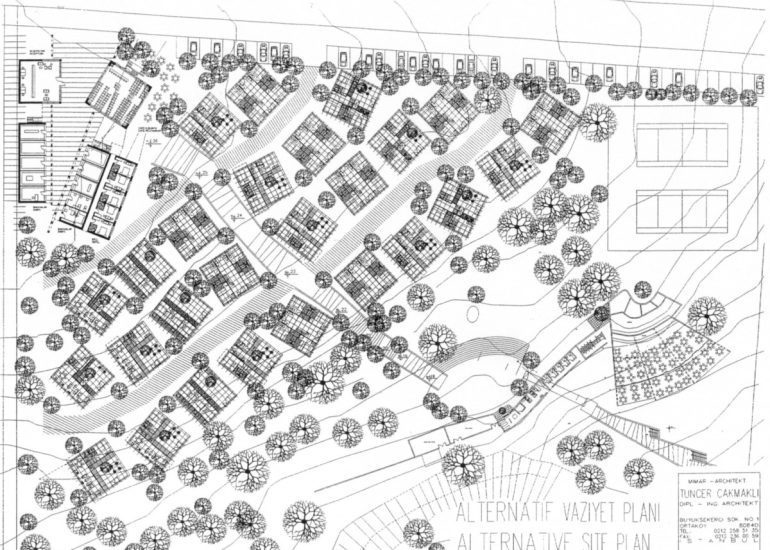
Architectural models are valuable tools that contribute to the design process, enhance communication, and support decision-making. Their tactile nature, scale representation, and visual impact make them an essential part of the architect’s toolkit.
Architecture, Trust, and the Fragility of Creative Work
Architecture is far more than the arrangement of walls, ceilings, and windows; it is the foundation of our human civilization, the visible expression of culture, dreams, and the ambitions of a society. It reflects not only functional necessities but also the subtle longings for aesthetics, harmony, and meaning. After the division of labor—where the architect, supported by education and experience, orchestrates the multitude of services—a special relationship emerges: that between architect and client, formed from trust, respect, and the shared vision of a building.
This trust is based on knowledge of the best possible execution—functional, economical, and unique in design. It is trust in the abilities of a team that works tirelessly, penetrating every sketch, model, and calculation, to transform the client’s vision into reality. In these hours, nights, and days of dedication, not only professionalism manifests itself, but also a quiet devotion to the very idea of building.
The presentation of designs to the client, accompanied by their high enthusiasm and amazement, is the moment when the idea comes alive. Here begins the detailed planning, carried by the fairly compensated work of the architect team, nurtured by the recognition and support that keeps creativity alive.
But what happens if the client suddenly finds the minimal fee too high and cancels the project without explanation? What happens to all the countless hours, the many nights, and the passion the team invested, even though the client showed the highest excitement during the presentation? This abrupt end is like the shattering of a precious glass—fragments that destroy the vision, the future, the planning, and the hope for cultural development.
In this breaking, the cruelty of creativity becomes evident when it is struck by a lack of understanding or appreciation. What remains of the best ideas and solutions is stolen or ignored, and those who were once creators find themselves robbed of their work. It is an act of destruction—not just of plans, but of the possibility of passing on culture, intelligence, and humanity. In such moments, humanity loses a piece of its future, a fragment of what makes it whole: the ability to bring beauty, function, and meaning into the world.
And yet architecture—despite all fragility, despite all shards—remains a monumental testimony of human thought. It demands from us not only creativity and knowledge but also courage, patience, and the ability to carry the vision forward even in the face of destruction. For in every failed project, in every abandoned dream, lies the silent reminder that culture, trust, and devotion are inextricably intertwined, and that humanity can scarcely survive without them.
Mimarlık, Güven ve Yaratıcı Çalışmanın Kırılganlığı
Mimarlık, duvarların, tavanların ve pencerelerin dizilişinden çok daha fazlasıdır; insan uygarlığımızın temeli, kültürün, hayallerin ve toplumun arzularının görünür ifadesidir. Sadece işlevsel gereklilikleri değil, aynı zamanda estetiğe, uyuma ve anlam arayışına dair ince özlemleri de yansıtır. Çalışma alanlarının bölünmesinden sonra – burada mimar, eğitim ve deneyimiyle çok sayıda hizmeti koordine eder – özel bir ilişki ortaya çıkar: mimar ile yapım sahibi arasındaki, güven, saygı ve ortak bir yapı vizyonuna dayanan ilişki.
Bu güven, en iyi uygulamanın bilgisine dayanır—fonksiyonel, ekonomik ve tasarım açısından benzersiz. Bu, yorulmak bilmeden çalışan bir ekibin yeteneklerine duyulan güvendir; her eskizi, her modeli, her hesaplamayı işleyerek yapım sahibinin vizyonunu gerçeğe dönüştürmek için. Bu saatlerde, gecelerde ve günlerde, sadece profesyonellik değil, aynı zamanda inşa etme fikrine sessiz bir bağlılık ortaya çıkar.
Tasarımın yapım sahibine sunumu, yüksek bir heyecan ve şaşkınlıkla karşılanması, fikrin canlandığı andır. İşte burada uygulama projeleri başlar; mimar ekibinin adil bir şekilde ücretlendirilmiş çalışmasıyla desteklenir ve yaratıcılığı canlı tutan tanınma ve destekle beslenir.
Peki ya yapım sahibi aniden en düşük ücreti bile yüksek bulup projeyi hiçbir gerekçe göstermeden iptal ederse ne olur? Tüm sayısız saatler, birçok gece ve ekibin yatırdığı tutku ne olur, sunum sırasında en yüksek heyecan gösterilmiş olmasına rağmen? Bu ani son, değerli bir camın kırılması gibidir—vizyonu, geleceği, planlamayı ve kültürel gelişim umudunu yok eden parçalar.
Bu kırılmada, yaratıcılığın acımasızlığı, anlayış veya takdir eksikliğiyle vurulduğunda açığa çıkar. En iyi fikirler ve çözümlerden geriye kalan çalınır veya görmezden gelinir ve bir zamanlar yaratıcı olanlar, emeklerinin elinden alındığını görür. Bu bir yıkım eylemidir—sadece planların değil, kültürü, zekâyı ve insanlığı aktarma olasılığının da yok edilmesidir. İnsanlık bu anlarda geleceğinin bir parçasını, onu insan yapan bir parçayı kaybeder: dünyaya güzellik, işlev ve anlam kazandırma yeteneğini.
Ve yine de mimarlık—tüm kırılganlığına, tüm parçalarına rağmen—insan düşüncesinin anıtsal bir tanığı olarak kalır. Bizden sadece yaratıcılık ve bilgi değil, aynı zamanda cesaret, sabır ve yıkım karşısında vizyonu sürdürme yeteneği ister. Çünkü her başarısız projede, her terk edilmiş hayalde, kültür, güven ve adanmışlığın ayrılmaz bir şekilde iç içe geçtiğini ve insanlığın onsuz ayakta kalmasının neredeyse imkânsız olduğunu sessizce hatırlatır.
——————————————————————————————————
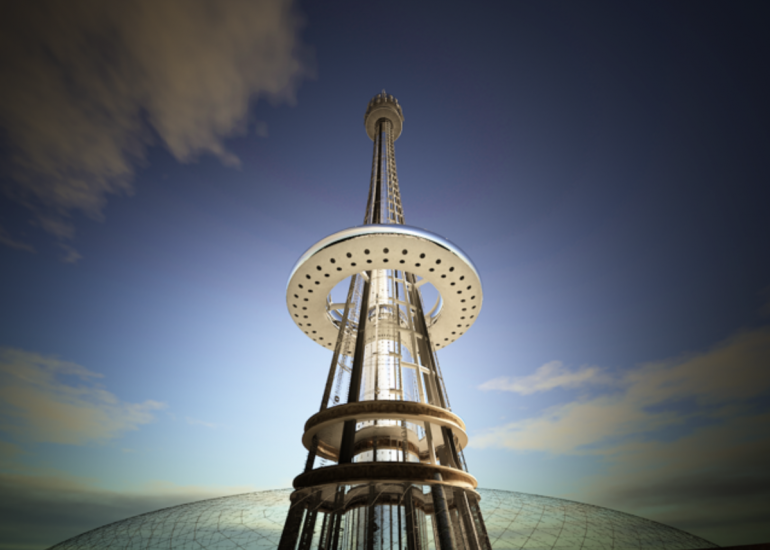
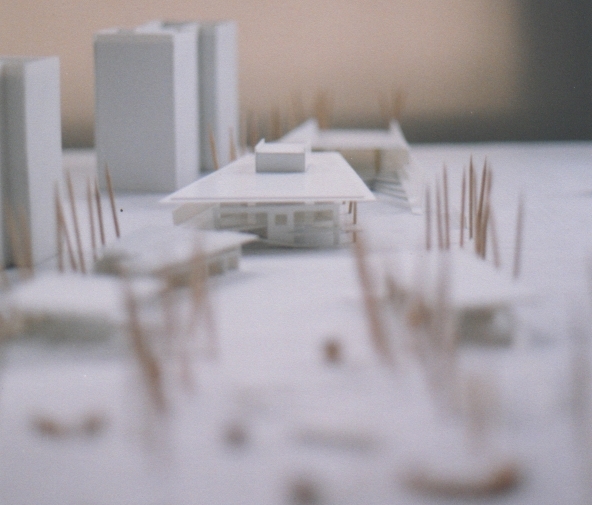
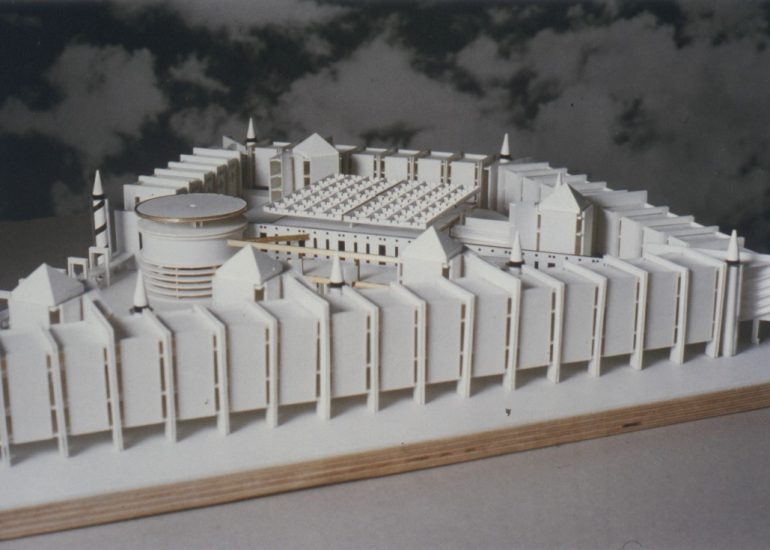
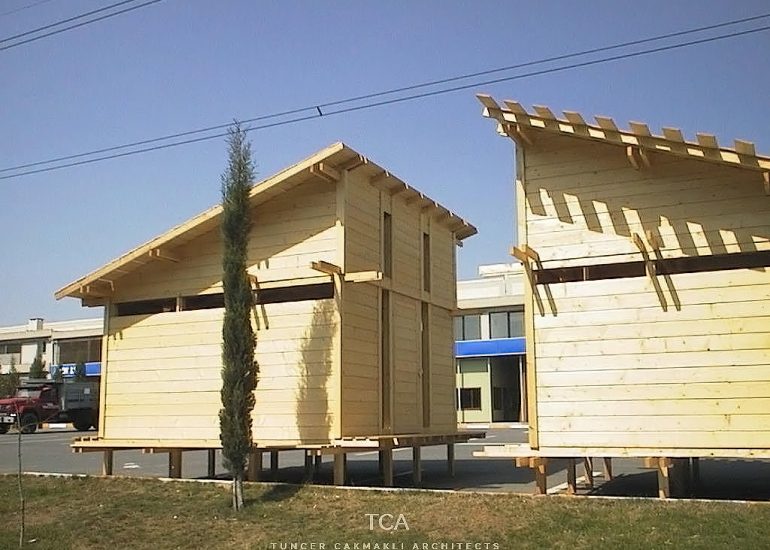
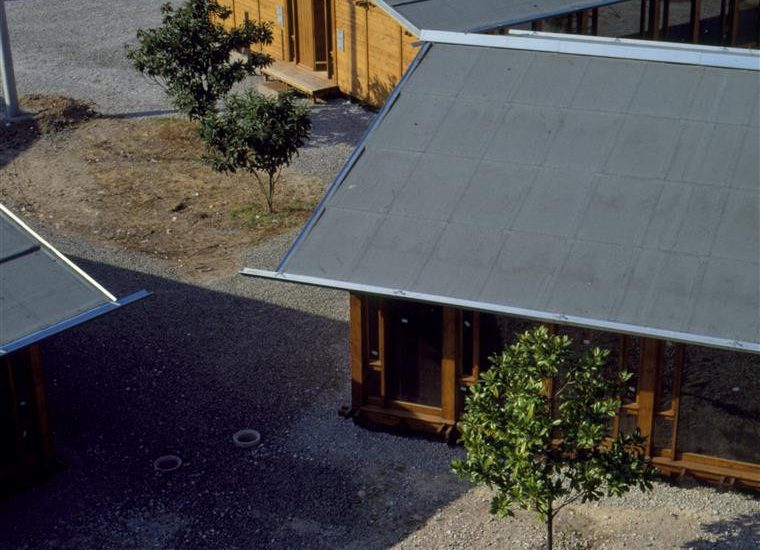
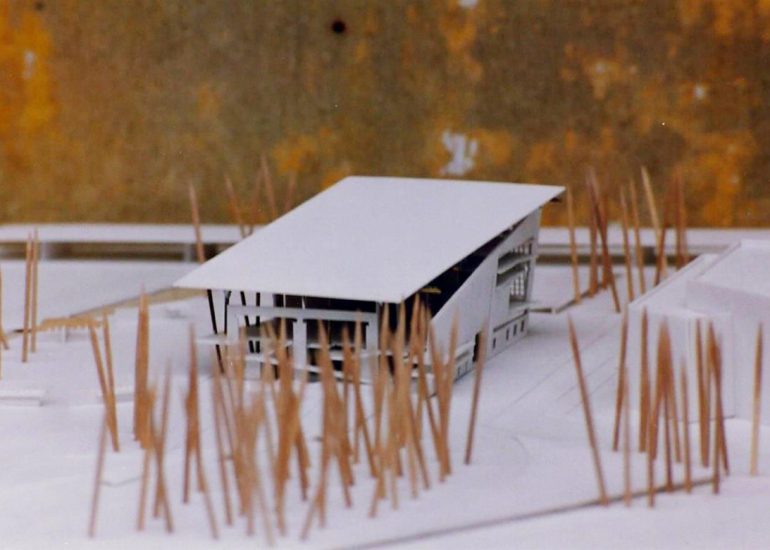
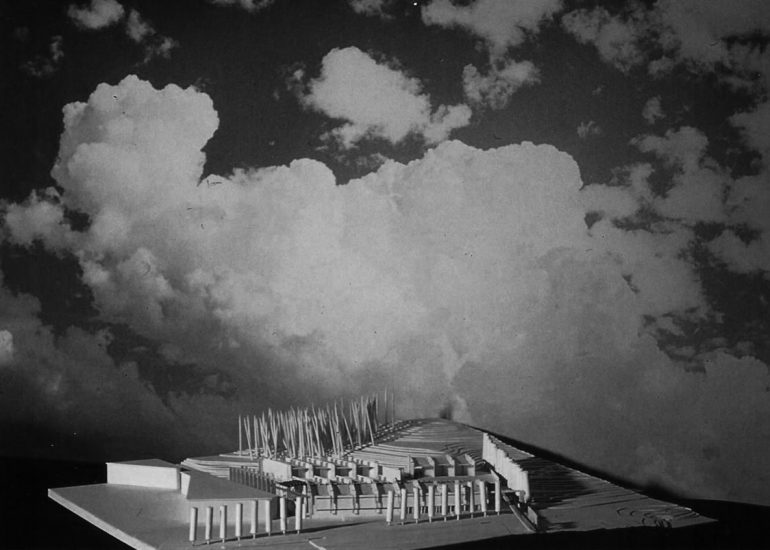
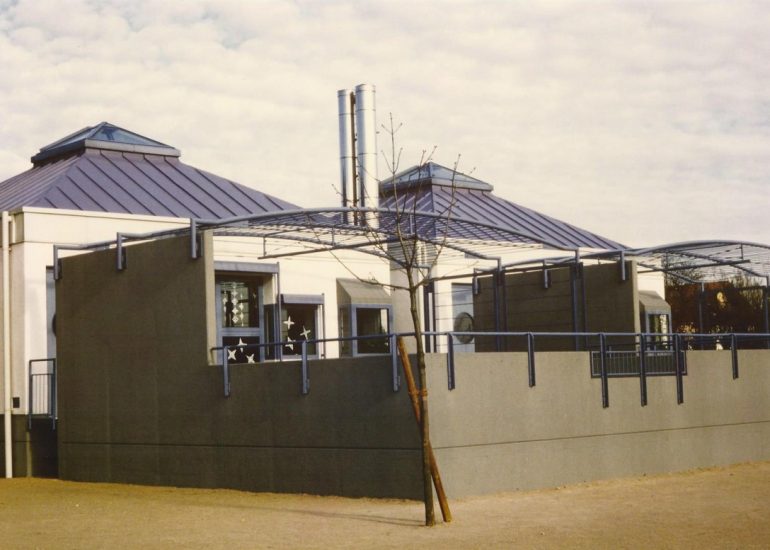
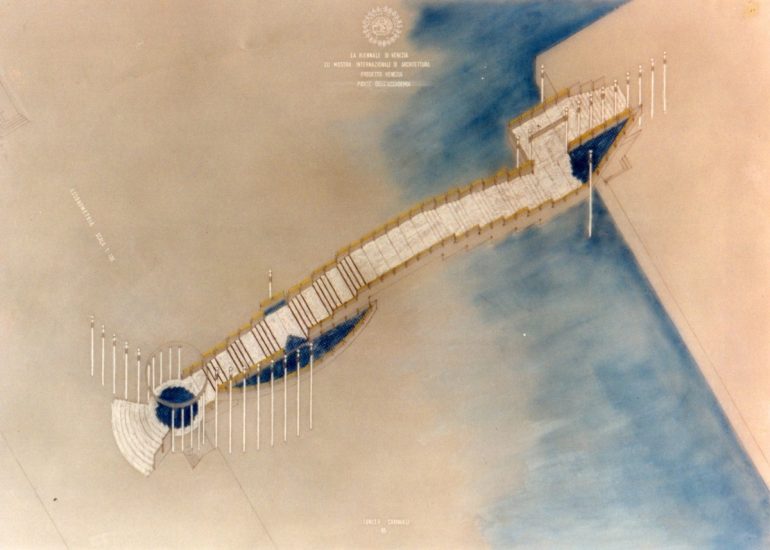
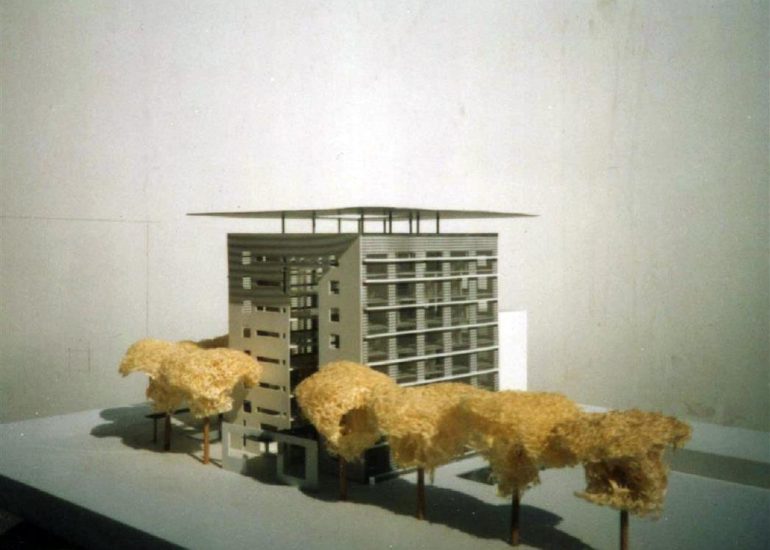
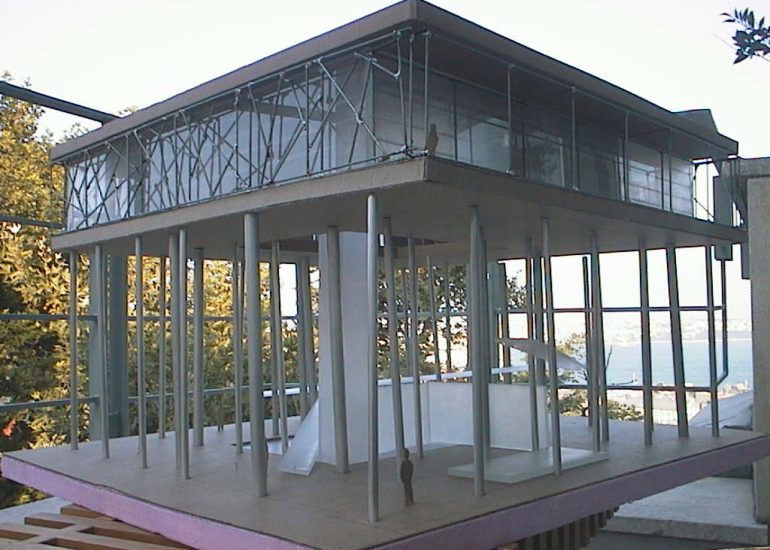
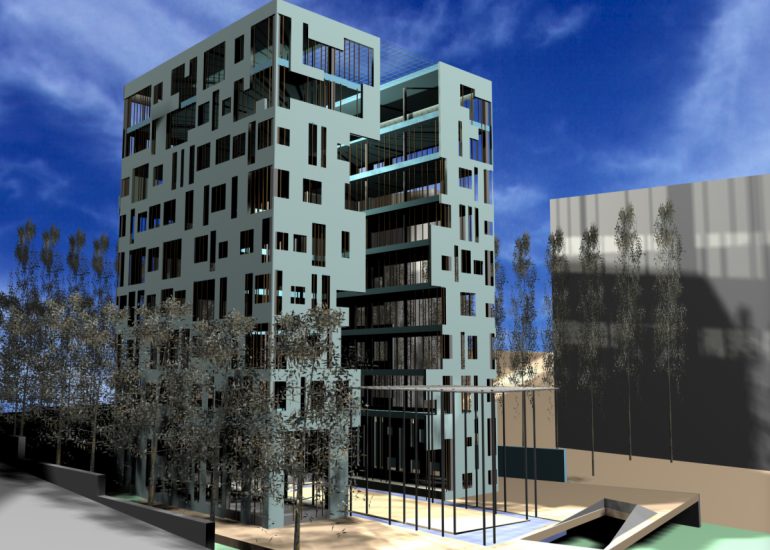
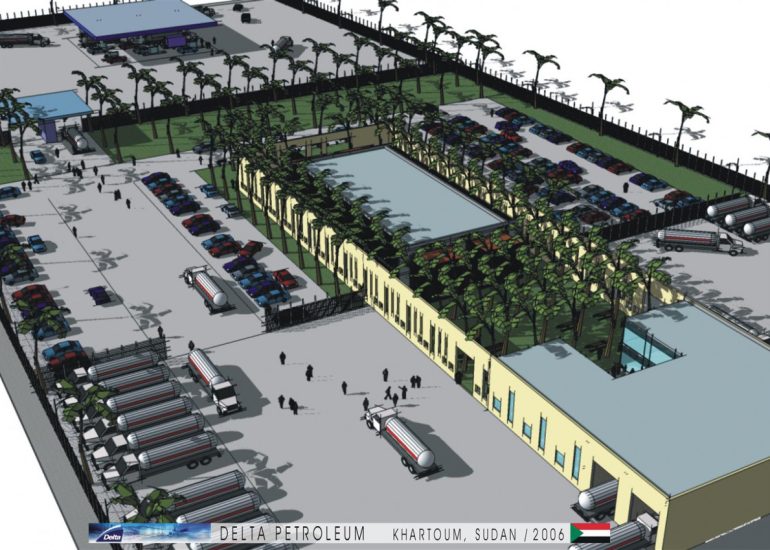
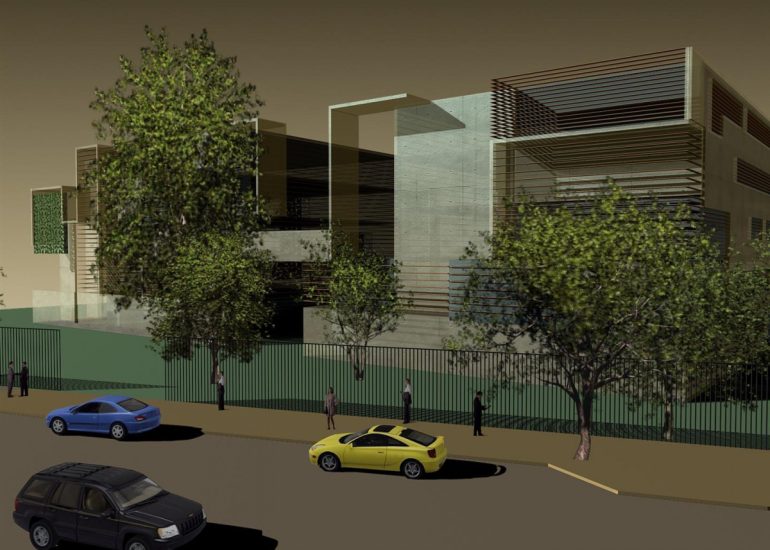
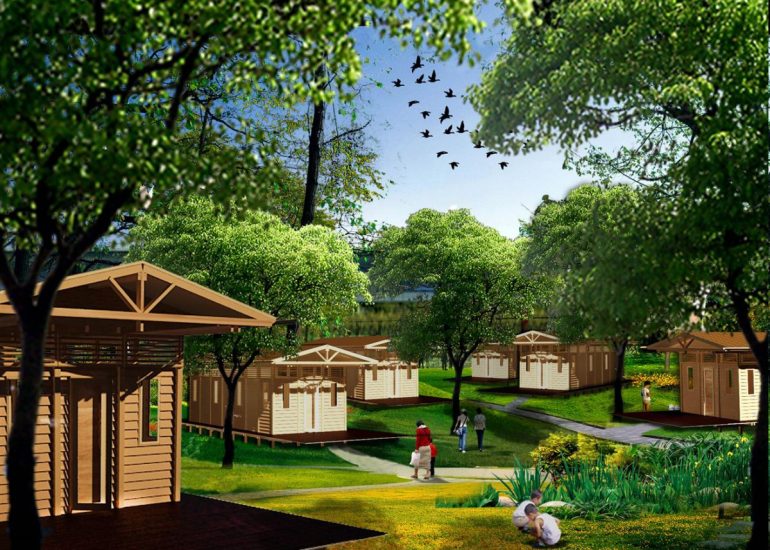
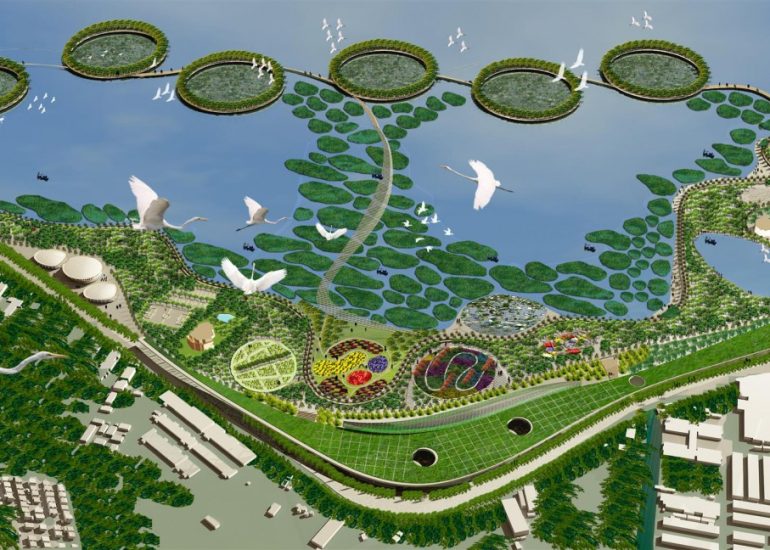
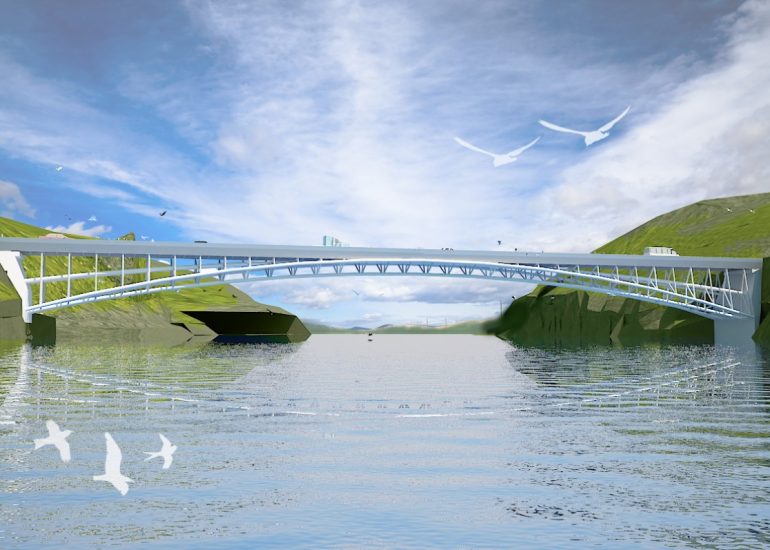
Visualization: Models provide a tangible and three-dimensional representation of architectural designs. They help architects and clients visualize the spatial relationships, proportions, and overall form of a building in a way that 2D drawings cannot fully convey. This aids in better understanding and appreciation of the design.
Scale Representation: Architectural models allow designers to present their ideas in scale, providing an accurate representation of the size and proportions of a building or space. This is crucial for understanding how the design will fit into its intended context and how people will experience it in the real world.
Design Exploration: Physical models facilitate the exploration of design alternatives. Architects can create multiple iterations of a model to study different design options and make informed decisions about the best approach. The hands-on nature of model-making encourages creativity and experimentation.
Client Communication: Models are effective communication tools when presenting designs to clients who may not have a background in architecture. A physical model allows clients to see, touch, and interact with the proposed design, making it more accessible and helping to convey the designer’s vision.
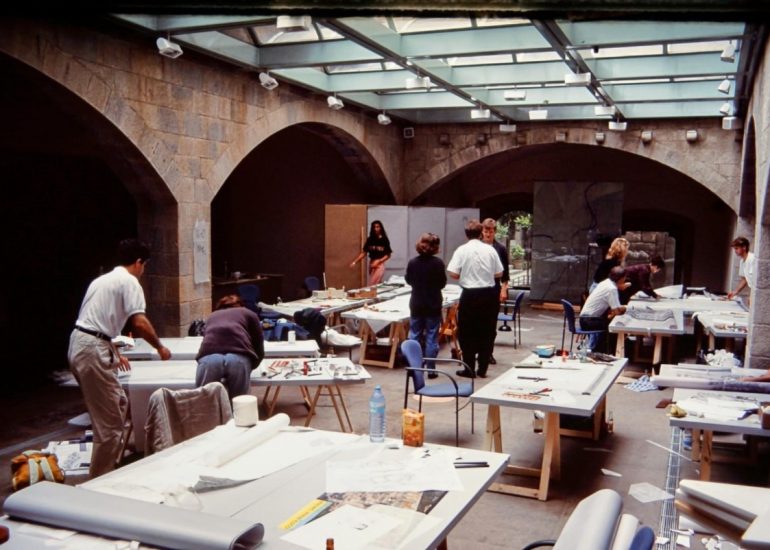
Team Collaboration: Architectural models encourage collaboration among design teams. They serve as a focal point for discussions and critiques, allowing team members to share ideas, identify strengths and weaknesses in the design, and work together towards refinements.
Educational Tool: Models are valuable educational tools for architecture students. They provide a hands-on learning experience, allowing students to translate their design ideas into physical form and gain a deeper understanding of architectural principles.
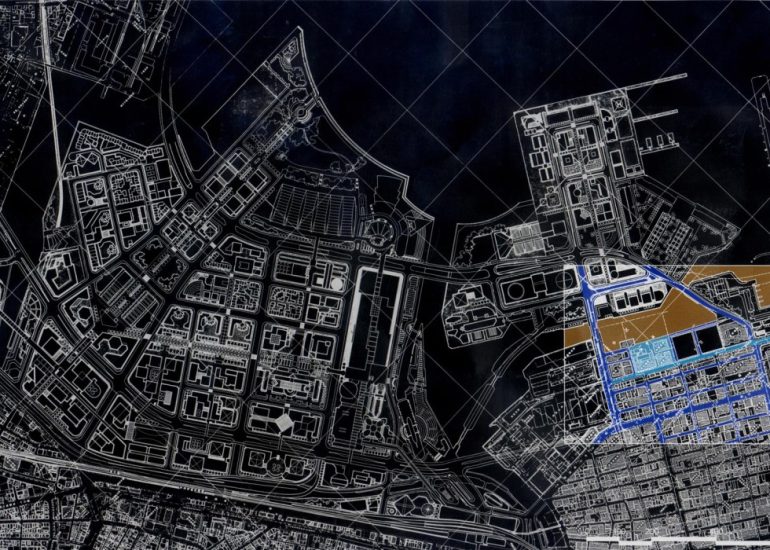
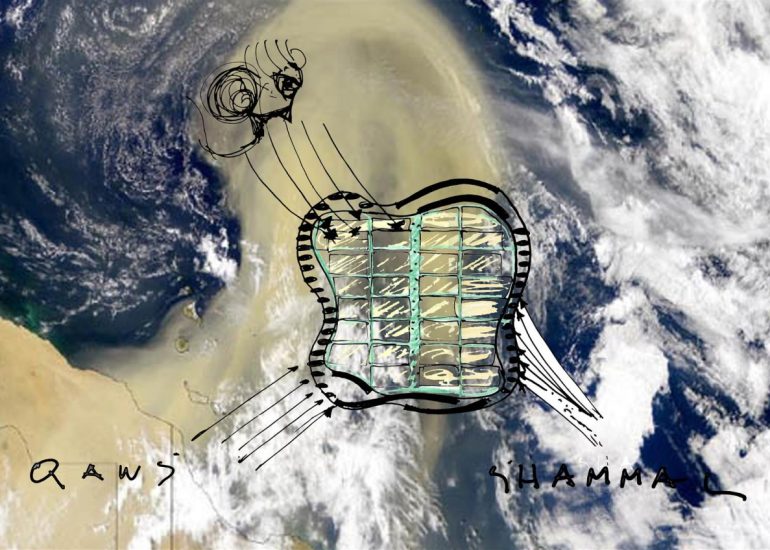
Site Analysis: Models can be used to study and analyze the relationship between a proposed building and its site. They help architects consider factors such as sunlight, wind patterns, and views, contributing to a more informed and site-specific design.
Presentation Quality: Architectural models enhance the quality of design presentations. Whether used in academic reviews, client meetings, or public presentations, models add a level of professionalism and sophistication to the communication of architectural concepts.
Material Exploration: Models allow architects to experiment with different materials and textures. This is particularly important in the early stages of design when material choices can significantly influence the aesthetic and functional aspects of a project.
Marketing and Promotion: Physical models are often used for marketing purposes, especially in real estate. Developers and architects use models to showcase proposed projects, helping to attract investors, buyers, and other stakeholders.
Photographic Documentation: Models provide a means of documenting the design process. Photographs of models can be included in portfolios, presentations, and project documentation, serving as a visual record of the evolution of a design.
The Art of Building Dreams: The Architecture of Dedication
In the quiet hum of the night, when the world is still, the architects of the future do not rest. They toil in the shadows, drawing not just lines but visions, sculpting not merely structures but dreams. The design is not a mere task; it is a battle fought with precision and passion. Like the pulse of a heart that never ceases, the architects work tirelessly to shape the soul of the future, knowing that each curve, each angle, each inch of space holds the power to change the world.
Hours become days. Days become months. The TCA team does not measure time in the conventional sense. It is measured in the moments of discovery when the impossible is realized, when a solution reveals itself after endless trials. The clock ticks, but it does not dictate their rhythm. They work as though they have all the time in the world, because they know: excellence does not come in the rush of minutes or the pressure of deadlines—it is born in the quiet perseverance of a team bound by a shared vision, unrelenting in their pursuit of perfection.
But what is perfection in architecture? It is not a static form, a rigid shape. It is fluid, alive, evolving. It is a process of constant adaptation, of searching deeper, reaching higher, and pushing further. It is in the balance between beauty and function, in the way a building speaks to those who walk through it, in the way light bends and flows across surfaces, casting shadows that dance and whisper. It is in the quiet details—the curvature of a stair, the alignment of a beam, the transition of textures—that the true meaning of architecture is felt.
In the still of the night, when the world outside is silent, the TCA architects work. They search for the perfect solution, the perfect form, the perfect dream. For in architecture, every design is a poem, and every line drawn is a verse in the endless pursuit of creating a better world.
It is not easy. The road is long, and the work is difficult. The obstacles are many, and the answers are never handed to them. But the TCA team continues. They continue because they know that the reward is not found in the final product alone—it is found in the journey.
The design is not a mere task; it is a battle fought with precision and passion. Like the pulse of a heart that never ceases, the TCA architects work tirelessly to shape the soul of the future, knowing that each curve, each angle, each inch of space holds the power to change the world.
Behind every blueprint, there is a saga of unending hours—hours that stretch like rivers flowing through time, with no destination except the perfect form. They search for the answer that lies in the unspoken corners of a drawing, the unseen harmony between materials, space, and light.